
In accounting, the margin of safety is the difference between actual sales and break-even sales. Managers utilize the margin of safety to know how much sales can decrease before the company or project becomes unprofitable. An advantage of the P/ V graph is that profits and losses at any point in time can be read directly from the vertical scale. Graphical analysis also enables managers to identify areas of profit or loss that would occur for a broad range of sales activities.
Break-Even Analysis Chart
This is beneficial for businesses that have been selling the same product at the same price point for years or businesses that are just beginning and are unsure of how to price their product. Break-even analysis can help determine those answers before you make any big decisions. For example, if the demand for your product is smaller than the number of units you’ll need to sell to breakeven, it may not be worth bringing the product to market at all. Finding your break-even point gives you a better idea of which risks are really worth taking. At the end of the day, your business needs to know what costs are impacting its ability to generate revenue. A break-even analysis can help you understand whether some products may be costing you more money than their worth.
Importance of Break-Even Point Analysis
Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for current assets definition lists and formula 2023 Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses.
What is the basic objective of break-even point analysis?
Once you’re above the break-even point, every additional unit you sell increases profit by the amount of the unit contribution margin. This is the amount each unit contributes to paying off fixed costs and increasing profits, and it’s the denominator of the break-even analysis formula. To find it, subtract variable costs per unit from sales price per unit.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
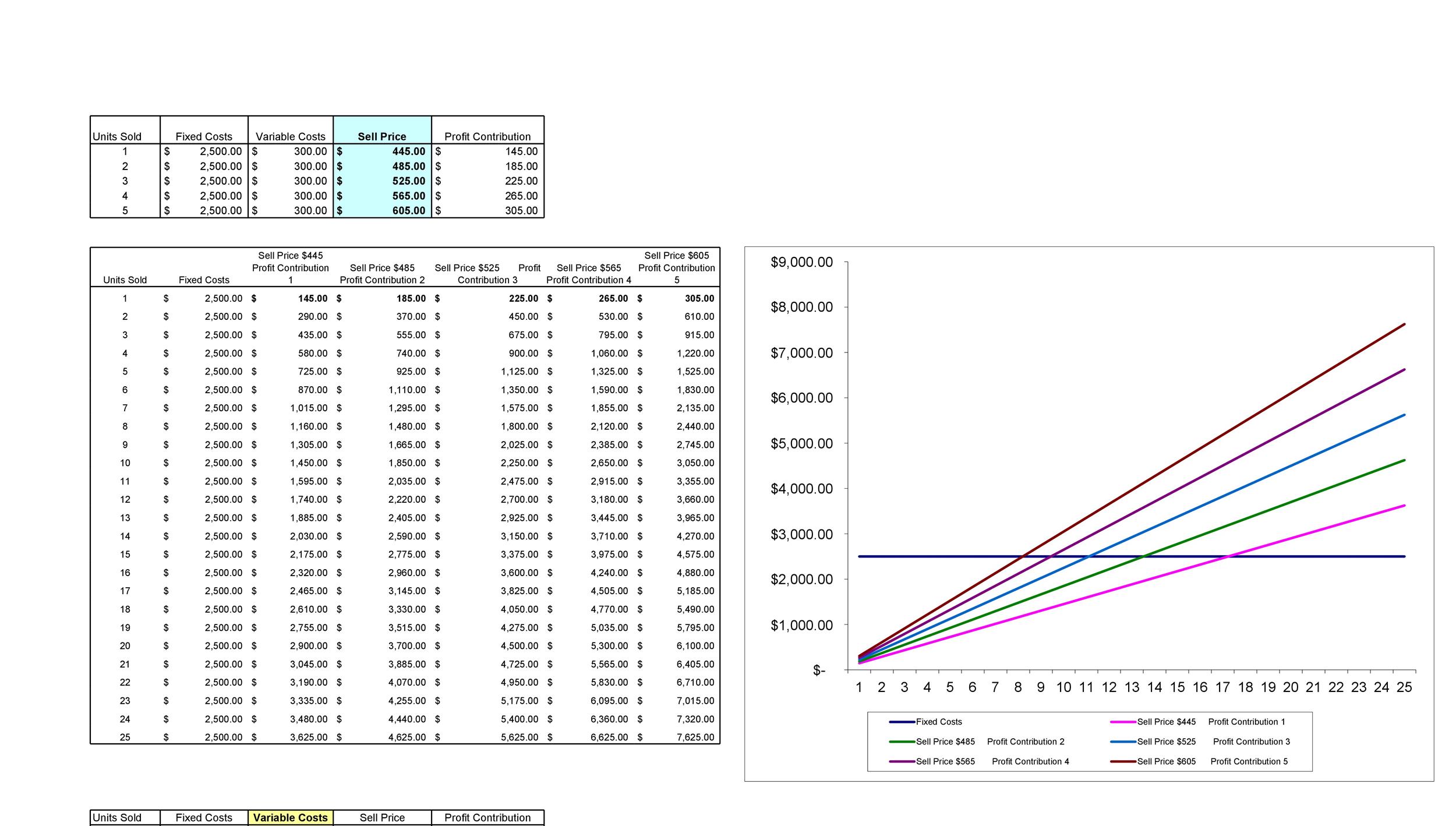
Break-even analysis involves a calculation of the break-even point (BEP). The break-even point formula divides the total fixed production costs by the price per individual unit less the variable cost per unit. Additionally, if the variable cost per unit can be reduced, the P/V graph shows the additional profits that can be expected at any given sales volume. Break-even analysis works well for short-term planning, like setting immediate sales goals or dedication to prices.
The more profit a company makes on its units, the fewer it needs to sell to break even. Upon selling 500 units, the payment of all fixed costs is complete, and the company will report a net profit or loss of $0. One limitation of break-even analysis is that it assumes selling prices will stay the same over time.
- In reality, prices often fluctuate due to market conditions, competition, or changes in demand.
- The interest being paid on all loans should be part of fixed costs, but it is shown as an expense in the profit & loss account.
- It is essential in determining the minimum sales volume required to cover total costs and break even.
- This lets them know how much product they need to sell to cover the cost of doing business.
Once you have the contribution margin, you then take the total fixed costs per unit and divide those costs by the contribution margin. This will give you the break-even number of units required to offset your costs. Variable costs also change as material, labor and other indirect variable expenses could increase or decrease as quantity changes.
Calculating the break-even point in sales dollars will tell you how much revenue you need to generate before your business breaks even. If you find yourself asking these questions, it’s time to perform break-even analysis. Read on to learn all about how break-even analysis can serve your small business. Whatever option you choose, the important thing is that you are aware of these metrics and actively using them. It will help you better understand the health of your business, make more strategic decisions, and ultimately grow your business.
In this breakeven point example, the company must generate $2.7 million in revenue to cover its fixed and variable costs. The break-even chart, also known as the Cost volume profit graph, is a graphical representation of the sales units and the dollar sales required for the break-even. On the vertical axis, the chart plots the revenue, variable cost, and the fixed costs of the company, and on the horizontal axis, the volume is being plotted. Now, when the number of units sold exceeds the breakeven point of 10,000 units, then the company Bag Ltd. would be making profits on the goods sold.
